static class Node {
int be, fin, dir;
Node(int be, int fin, int dir) {
this.be = be;
this.fin = fin;
this.dir = dir;
}
}2528번: 사다리
첫 번째 줄에 층 수 N (1<=N<=3,000)과 층의 길이 L (1<=L<=3,000, L은 짝수)이 주어진다. 가장 아래층은 1층이고 가장 위층은 N층이다. 다음 N개의 줄 중 i번째 줄에는 i층의 막대기의 길이 l (1<=l<=L, l은
www.acmicpc.net
1. 유형
구현
2. 풀이
- 입력받기 (input)
- 올라갈 수 있는 층 탐색 (up)
- 1초에 한칸씩 이동 (move)
크게 위와 같은 함수를 구현할 수 있으면 된다.
구현 난이도는 그렇게 어렵지 않지만 처음에 입력값 전처리를 하는것이 중요하다.
static class Node {
int be, fin, dir;
Node(int be, int fin, int dir) {
this.be = be;
this.fin = fin;
this.dir = dir;
}
}위 처럼 begin, fin, dir(시작, 끝값, 방향)을 클래스로 입력 받는다.
층을 올라갈 수 있는 경우의 수는
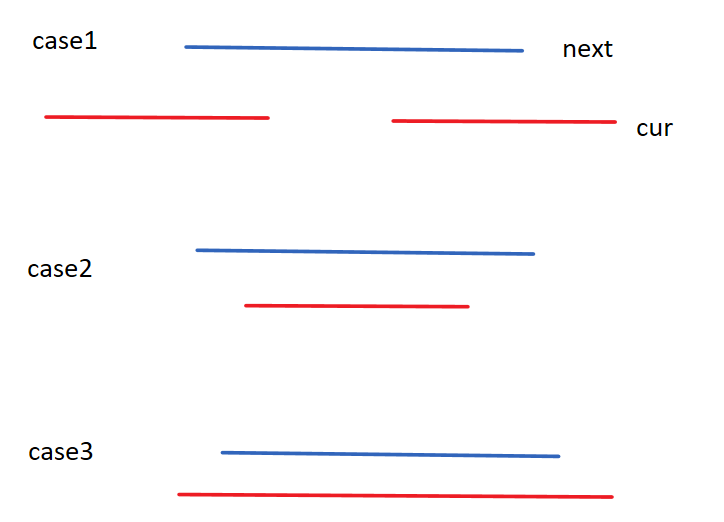
이런 식으로 3가지 경우가 나올 수 있다. 시작점과 끝점을 비교해서 경우를 나타내자
3. 디버깅 실수
가장 처음 생각한 풀이는 모든층과 길이를 배열로 전처리를 하는것이다.
시간이 지날때마다 한칸씩 슬라이딩 윈도우를 해서 구현하려고 했다. 이러면 아마 시간초과가 날 것이다.
그래서 이 문제에서 가장 중요한점은 처음에 시작과 끝점을 설정하는 점이다.
4. 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer st;
static int N, L, cur_stair, res;
static boolean flag = false;
static class Node {
int be, fin, dir;
Node(int be, int fin, int dir) {
this.be = be;
this.fin = fin;
this.dir = dir;
}
}
static Node node[];
static void input() throws IOException {
st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
N = Integer.valueOf(st.nextToken());
L = Integer.valueOf(st.nextToken());
node = new Node[N + 1];
cur_stair = 1;
res = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
int l = Integer.valueOf(st.nextToken());
int dir = Integer.valueOf(st.nextToken());
if (dir == 0) {
node[i] = new Node(0, l, dir);
} else {
node[i] = new Node(L - l, L, dir);
}
}
}
static void up() {
while (true) {
if (cur_stair == N) {
flag = true;
break;
}
Node cur = node[cur_stair];
Node next = node[cur_stair + 1];
if ((cur.fin >= next.be && cur.fin <= next.fin) || cur.be >= next.be && cur.be <= next.fin) {
cur_stair++;
} else if (cur.be >= next.be && cur.fin <= next.fin) {
cur_stair++;
} else if (cur.be < next.be && cur.fin > next.fin) {
cur_stair++;
} else
break;
}
}
static void move() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Node cur = node[i];
if (cur.dir == 0) {
cur.be++;
cur.fin++;
if (cur.fin == L) {
cur.dir = 1;
}
} else {
cur.be--;
cur.fin--;
if (cur.be == 0) {
cur.dir = 0;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
while (true) {
res++;
up();
move();
if(flag) {
System.out.print(res);
break;
}
}
}
}
'알고리즘 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 - 16137 견우와 직녀 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
|---|---|
| 백준 - 20061 모노미노도미노2 (0) | 2021.03.06 |
| 백준 - 1360 되돌리기(Java) (0) | 2021.02.28 |
| 백준 - 3055 탈출(Java) (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| 백준 9322 - 철벽보안 알고리즘(Java) (0) | 2021.01.31 |
